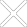1. Introduction
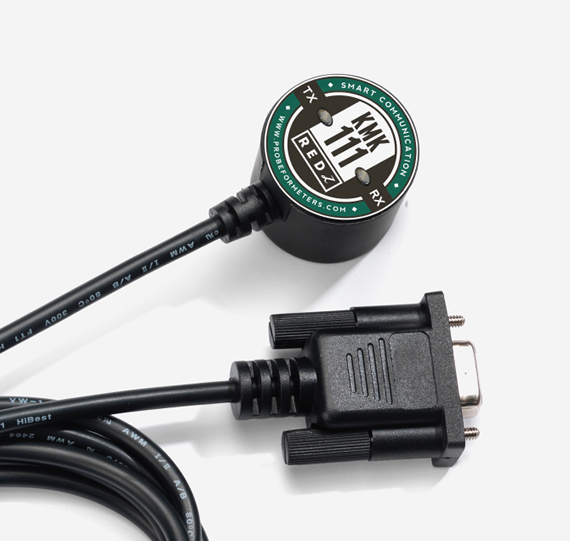
A Meter Reading Optical Probe is a specialized device used for reading utility meters (such as electric, gas, or water meters) that use optical communication ports to transmit data. These probes are typically used in Automated Meter Reading (AMR) or Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) systems, where they allow for direct and non-intrusive access to meter data. The probe connects to the meter's optical port, retrieves the consumption data, and transmits it to a handheld device, laptop, or central monitoring system for processing.
Optical probes help utilities collect data more efficiently, reducing the need for manual meter readings, which are time-consuming and prone to error.
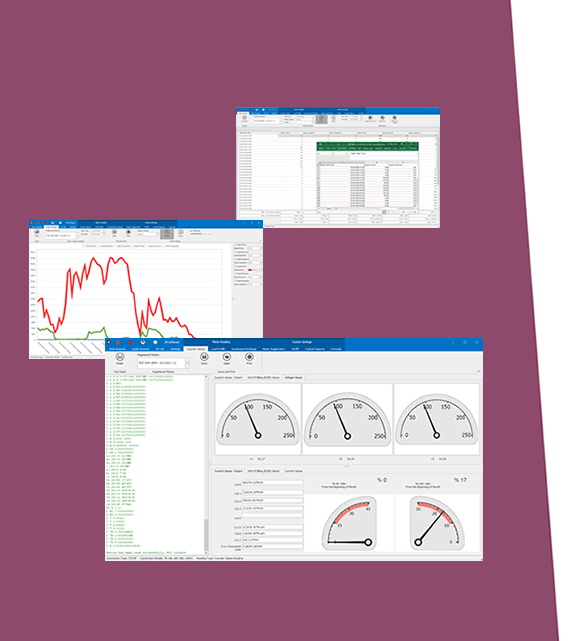
Reference : https://probeformeters.com/brochure/brochure_kmk116_en.pdf
2. How Does a Meter Reading Optical Probe Work?
The probe typically uses infrared technology to communicate with the meter. It aligns with the optical port on the meter and establishes a two-way communication channel. This allows it to:
- Read consumption data: Capture information like energy, water, or gas usage.
- Configure the meter: In some cases, technicians can use the optical probe to reconfigure settings on the meter.
- Verify meter operations: Ensure that the meter is functioning correctly or troubleshoot any issues.
3. Key Features of a Meter Reading Optical Probe
- Magnetic Base: Many optical probes come with magnetic heads that attach securely to the meter’s optical port, ensuring stable communication.
- Compatibility: Probes are designed to work with specific meter brands and models, following standards such as ANSI or IEC.
- Portable and Easy to Use: Probes are typically lightweight and designed for ease of use by field technicians.
- USB, Serial or Wireless (Bluetooth or WiFi) Interface: Most optical probes connect to a handheld reader or a computer via USB or serial port.
4. Where to Use a Meter Reading Optical Probe
1. Utility Companies (Electricity, Water, Gas)
The primary use case for optical probes is in the utility sector. Utility companies use these devices to collect data from a variety of meters that measure consumption of electricity, water, or gas. Probes offer a quick and reliable way to retrieve data, especially for meters located in difficult-to-access areas.
2. Automated Meter Reading (AMR) Systems
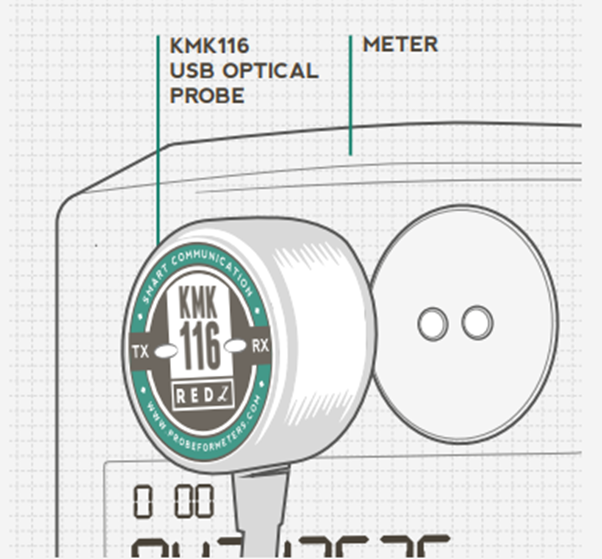
In AMR systems, the optical probe serves as a crucial tool for retrieving data. It provides direct communication with the meter, allowing technicians to collect readings without needing to manually inspect the meter’s display.
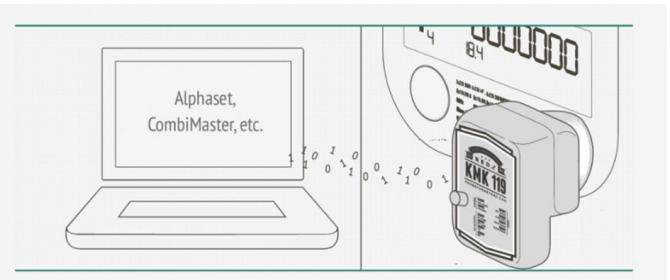
Reference: https://probeformeters.com/en/manuals/bluetooth-optical-probe-user-manual
3. Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
For more advanced systems, optical probes can be used to interface with meters to enable not only reading data but also uploading configuration changes. They are helpful in setting up meters for AMI systems where remote monitoring and control are required.
4. Smart Metering Projects
When upgrading from traditional to smart meters, optical probes can be used during installation and testing. They allow technicians to ensure proper configuration and communication between the meter and the network.
5. Meter Maintenance and Diagnostics
Optical probes can be used to perform diagnostics and maintenance on meters. When there are issues with data transmission or suspected malfunctions, a technician can use the probe to connect directly to the meter and verify its operation.
6. Field Technicians & Metering Contractors
Optical probes are essential tools for technicians who are tasked with collecting meter readings or performing configuration updates in the field. They are highly portable and easy to use, making them perfect for regular or one-off meter inspections.
5. Where Not to Use a Meter Reading Optical Probe
1. Meters Without Optical Ports
Some utility meters, especially older models, do not have optical communication ports. In such cases, a meter reading optical probe cannot be used, and manual readings or other methods (like RF or network communication) must be employed.
2. Fully Networked Smart Meters with Remote Reading
In systems where smart meters are fully integrated into a wireless or wired network (such as AMI systems with real-time remote monitoring), the need for optical probes is greatly reduced. Remote access via the network can provide meter readings directly to the central system, eliminating the need for physical interaction with the meter.
3. Harsh or Inaccessible Environments
In areas where the meter’s optical port is difficult to access due to environmental conditions (e.g., submerged, underground, or in hazardous areas), the use of an optical probe may not be feasible. In these cases, meters equipped with RF or other wireless communication technologies might be a better choice.
4. Meters with Sealed or Tamper-Resistant Optical Ports
Some meters may have tamper-resistant seals over their optical ports, limiting access for security reasons. In these situations, unless permission is granted to break the seal, using an optical probe may not be possible.
5. Meters Requiring Wireless Communication
For meters that are designed to work with wireless protocols like LoRa, Zigbee, or cellular networks, using an optical probe is impractical. These meters are designed to send readings directly over a network without the need for physical connection.
6. Conclusion
Meter reading optical probes are ideal for utility companies and technicians who need to collect data from meters equipped with optical ports. They are particularly useful in Automated Meter Reading (AMR) and Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) systems, as well as in smart metering projects, meter maintenance, and field diagnostics.
Optical probes are not useful for meters without optical ports, fully networked smart meters that support remote reading, or in locations where the meter’s optical port is difficult to access. Additionally, meters with wireless communication capabilities or tamper-resistant designs may render optical probes unnecessary.