1.Introduction
The DLMS/COSEM protocol, short for Device Language Message Specification/Companion Specification for Energy Metering, is a widely adopted international standard used in energy metering and smart grid communication systems. It is designed to provide interoperability, scalability, and flexibility in managing and monitoring energy consumption. This protocol is managed by the DLMS User Association (DLMS UA) and complies with IEC 62056 standards, ensuring global compatibility.
2. What is DLMS/COSEM?
DLMS/COSEM is a two-part protocol:
1. DLMS (Device Language Message Specification): Defines the communication rules and methods for exchanging data between devices.
2. COSEM (Companion Specification for Energy Metering): Specifies the data model and the way data is organized and accessed.
Together, DLMS/COSEM provides a structured and efficient framework for smart energy metering, ensuring seamless communication between meters, systems, and utilities.
3. Core Components of DLMS/COSEM
1. COSEM Object Model:
o Data is organized into objects (e.g., current energy consumption, historical data, alarms).
o Each object is identified by an Object Identification System (OBIS) code, which categorizes and standardizes the data.
2. Communication Profiles:
o Lower Layers: DLMS/COSEM supports multiple physical and link-layer technologies, such as PLC (Power Line Communication), GPRS, and TCP/IP.
o Application Layer: Handles security, session management, and object access using a client-server model.
3. Security Features:
o Includes authentication, encryption, and access control to protect data integrity and privacy.
o Meets modern security standards for smart grids.
4. Interoperability:
o Enables devices from different manufacturers to communicate seamlessly.
o Facilitates integration across diverse energy ecosystems.
4. How Does DLMS/COSEM Work?
1. Communication Setup:
o A client (e.g., utility management system) connects to a server (e.g., smart meter).
o The client initiates a session using secure protocols.
2. Data Exchange:
o The client requests specific data objects (e.g., total energy usage).
o The server provides data in a standardized format, ensuring clarity and accuracy.
3. Data Interpretation:
o OBIS codes categorize the retrieved data (e.g., 1.0.1.8.0.255 for active energy).
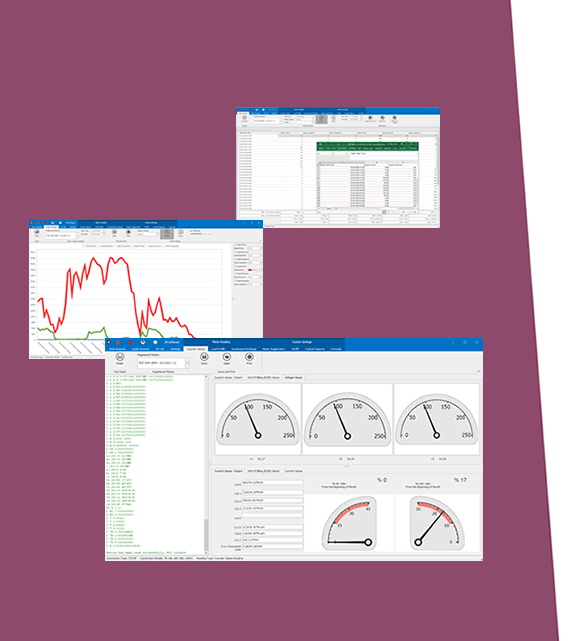
o The client system processes and visualizes this data for monitoring, billing, or analysis.
5. Applications of DLMS/COSEM
1. Smart Metering:
o Used for electricity, gas, water, and heat meters.
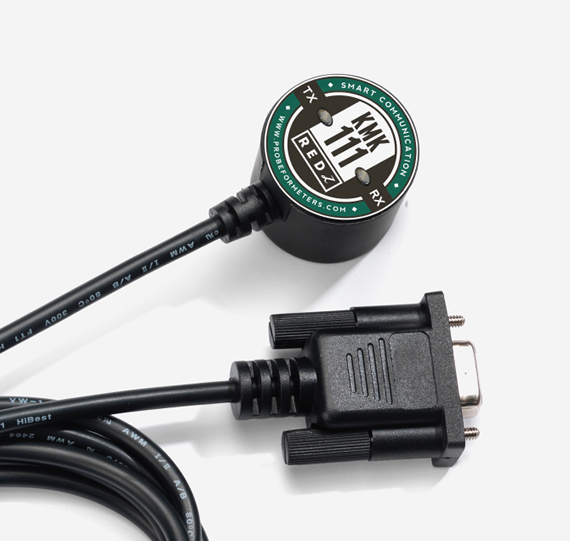
o Enables real-time monitoring, remote meter reading, and accurate billing. REDZ KMK series optical probes, such as the KMK118 and KMK119, are compatible with the DLMS/COSEM protocol. These probes are designed to support both IEC 62056-21 and DLMS/COSEM standards, making them versatile tools for energy meter communication.


2. Demand Response Management:
o Helps utilities balance energy supply and demand by analyzing consumption patterns.
3. Energy Theft Detection:
o Advanced security and data logging capabilities help identify unauthorized usage.
4. Smart Grid Integration:
o Facilitates communication between distributed energy resources and grid operators.
6. Advantages of DLMS/COSEM
• Interoperability: Universally accepted and supported by major meter manufacturers.
• Scalability: Suitable for small residential setups to large industrial applications.
• Flexibility: Supports multiple communication technologies.
• Robust Security: Protects sensitive user data.
• Standardization: Ensures consistency and reliability in energy metering.
7. Challenges
• Implementation Complexity: Requires expertise in setting up and configuring DLMS/COSEM systems.
• Cost: Advanced meters and communication infrastructure can be expensive.
• Training Needs: Personnel need proper training to manage and interpret data effectively.
8. Conclusion
The DLMS/COSEM protocol is a cornerstone of modern energy metering and smart grid solutions, enabling efficient, secure, and standardized communication. As energy systems become more interconnected, the protocol’s role in ensuring reliability and scalability will only grow. Utilities, manufacturers, and policymakers increasingly rely on DLMS/COSEM to meet the evolving demands of energy management and sustainability.
By leveraging DLMS/COSEM, the energy industry can achieve higher efficiency, better resource management, and improved customer satisfaction, paving the way for a smarter, more sustainable future.