1.Introduction
In the rapidly evolving world of industrial automation and IoT, efficient monitoring and control of remote I/O devices have become paramount. MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) protocol has emerged as a reliable and lightweight messaging standard, offering robust communication for IoT applications. By integrating MQTT servers with advanced I/O devices such as the REDZ HUR Series Remote I/O, businesses can achieve seamless data exchange, enhanced control, and improved operational efficiency.
2.Why Use MQTT for Remote I/O?
MQTT is specifically designed to enable efficient communication in resource-constrained environments. Key benefits include:
1. Lightweight Protocol: MQTT minimizes bandwidth usage, making it ideal for environments with limited network capacity.
2. Reliable Communication: Features like Quality of Service (QoS) levels ensure message delivery even in unstable network conditions.
3. Scalability: MQTT servers can handle thousands of devices and clients, providing a scalable solution for IoT ecosystems.
4. Real-Time Updates: Publish/subscribe architecture enables instant communication between devices and applications.
3. REDZ HUR Series Remote I/O Devices
The REDZ HUR Series Remote I/O devices are designed to integrate seamlessly with MQTT servers. These devices offer:
• Versatile I/O Options: Support for digital inputs/outputs, analog inputs, and relay outputs, enabling flexibility across applications.
• Robust Build: Built to withstand challenging industrial environments, ensuring reliable performance.
• Simplified Integration: Plug-and-play compatibility with MQTT servers reduces deployment time and costs.
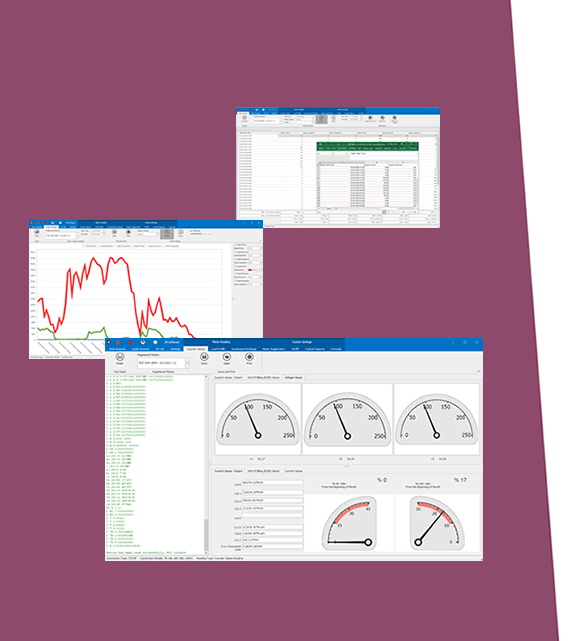
• Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts: Collect and transmit data to MQTT servers for instant processing and actionable insights.
4. Use Cases for MQTT and REDZ HUR Series
Combining MQTT servers with REDZ HUR Series devices unlocks numerous possibilities across industries:
1. Industrial Automation: Real-time monitoring and control of production lines, machinery, and energy usage.
2. Smart Buildings: Manage HVAC systems, lighting, and security devices efficiently through MQTT-enabled I/O modules.
3. Utilities Management: Monitor and control water flow, gas distribution, and electricity grids with minimal latency.
4. Smart Agriculture: Automate irrigation, monitor soil conditions, and control equipment across large fields.
5. Environmental Monitoring: Measure air quality, temperature, and humidity, transmitting data to central systems for analysis.
5. Simplified Integration with MQTT Servers
REDZ HUR Series devices are optimized for seamless communication with MQTT servers, enabling a unified platform for monitoring and controlling remote assets. Data collected from these devices can be processed, visualized, and acted upon in real-time, allowing businesses to make informed decisions and improve operations.
6. Benefits of Using MQTT with REDZ HUR Series
1. Cost Efficiency: The lightweight nature of MQTT reduces infrastructure costs, while REDZ HUR devices offer affordable and reliable hardware.
2. Enhanced Reliability: MQTT’s QoS settings and the rugged design of REDZ HUR devices ensure uninterrupted operations.
3. Real-Time Data Insights: Publish/subscribe architecture allows immediate access to critical data.
4. Future-Ready Solutions: The combination of MQTT and REDZ HUR devices ensures scalability and adaptability for evolving IoT needs.
7. Conclusion
Monitoring and controlling remote I/O devices via MQTT servers is a powerful approach to modern industrial and IoT applications. The integration of the REDZ HUR Series Remote I/O devices with MQTT technology offers unparalleled flexibility, real-time monitoring, and operational efficiency. By adopting this solution, businesses can stay ahead in the IoT revolution and achieve greater control over their assets.